Pseudouridine: What is it and Why Should you Care?
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded for discovering use of Pseudouridine to suppress immune responses to synthetic mRNA, and use of that discovery in COVID-19 mRNA vaccines.
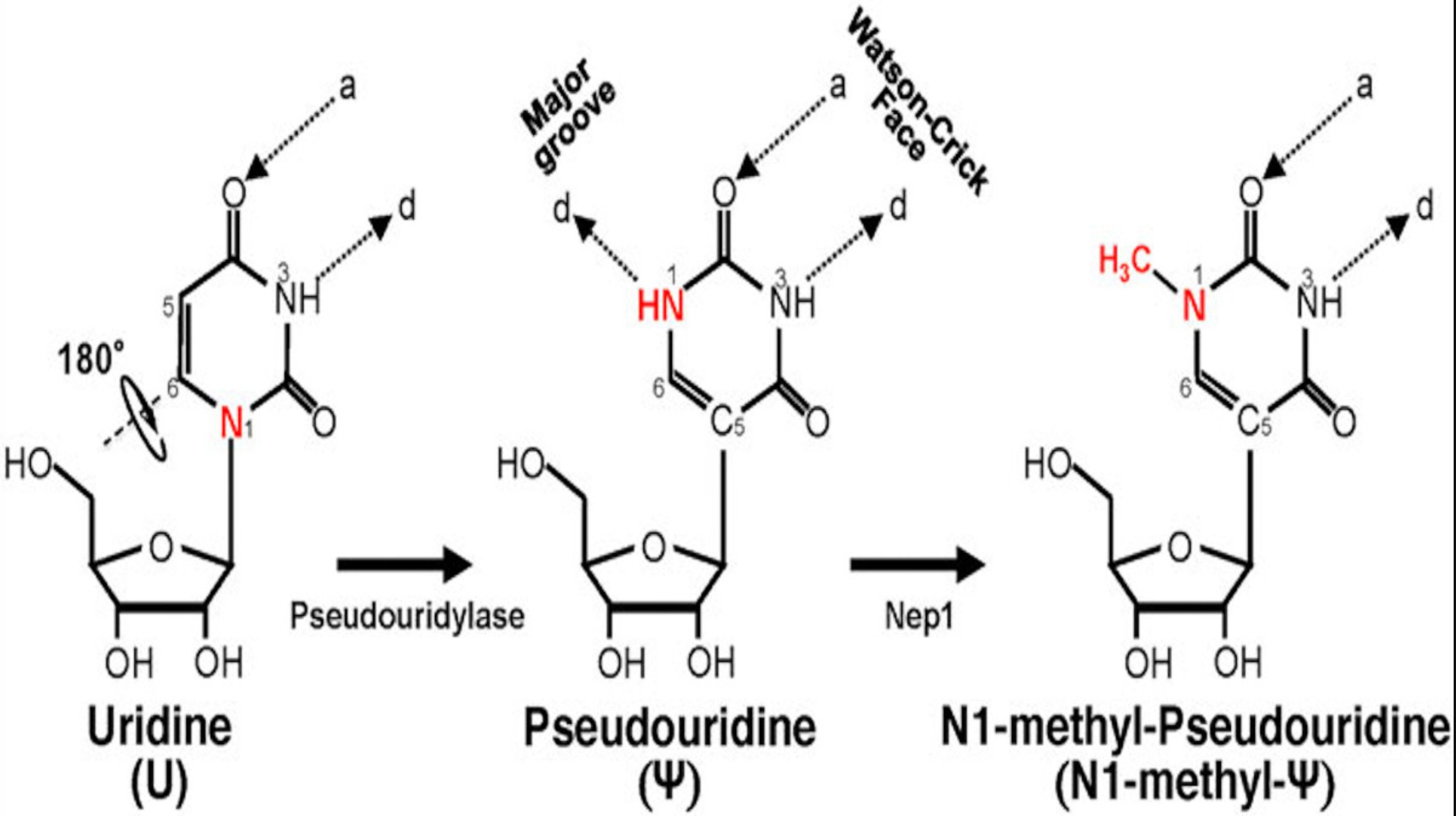
Uridine, one of the four key components of natural RNA and mRNA (A, U, G, C), shown together with the structures of Pseudouridine and N1-methyl-Pseudouridine
Background
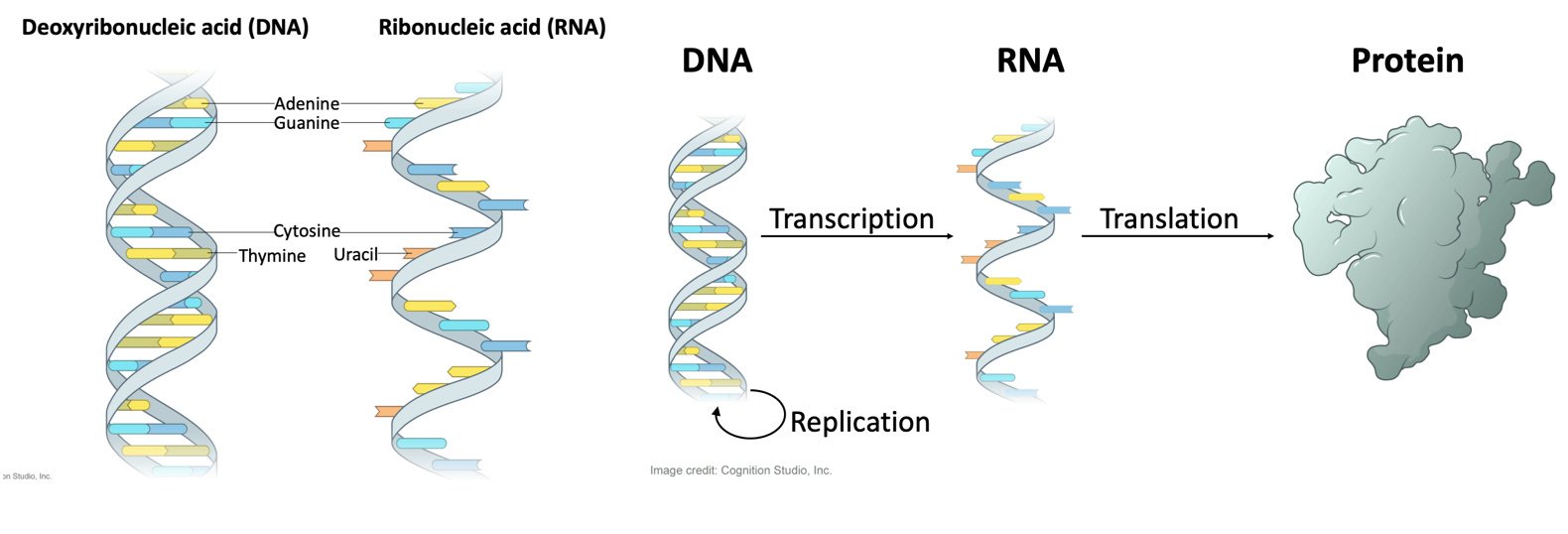
Natural RNA, including mRNA, consists of a polymerized string of four different compounds - A, U, G, C. U = Uridine. There are many different natural forms of RNA in cells, but in general, DNA makes mRNA, and mRNA makes protein (polypeptide).
In cells after polymerization, in some mRNA there are precisely controlled modifications to the “U” compounds (bases) to convert them to a different compound, called pseudouridine. The presence of such precise pseudouridine modifications regulate many aspects of mRNA biology, including how long it persists in the cell before being degraded, the structures that it forms when folding, how efficiently it is turned into protein (translated), and the activity of certain cell types containing this modified mRNA when responding to inflammation. Pseudouridine messages an anti-inflammatory (which is to say immunosuppressive) signal to cells.
Kariko and Weissman recently received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their their discovery that replacement of synthetic pseudouridine for uridine throughout synthetic mRNA reduces the inflammation triggered when this synthetic mRNA is delivered into the cells of animals using self-assembling cationic lipid delivery particles, and specifically the use of that discovery to enable the rapid development of the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 mRNA “vaccines” that have been deployed throughout the world.
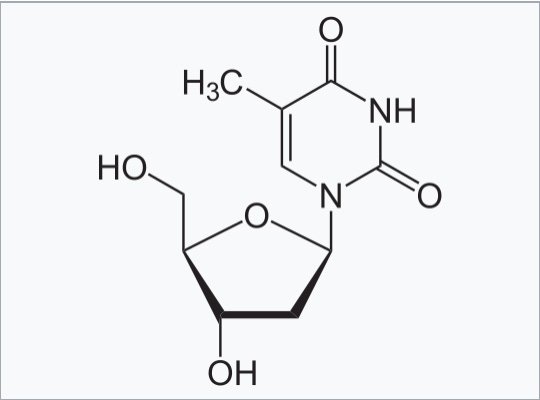
In a break with standard regulatory practice, under the EUA process the FDA did not require rigorous assessment of the pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, safety, toxicity, reproductive toxicity or any other aspect of synthetic mRNA incorporating pseudouridine for human (or animal) use. Furthermore, the synthetic pseudo-mRNA (which is very different in many ways from naturally produced mRNA) manufactured and dosed into humans throughout the globe does not even contain pseudouridine. Instead, it incorporates a synthetic molecule which is even more potent that naturally occurring pseudouridine, called N1 Methyl pseudouridine, which is structurally more closely related to the molecule Thymidine, which is found in DNA (not RNA).
Chemical structure of Thymidine, one of the four key components of DNA (A, T, G, C)
As a consequence of this decision by FDA, which was then followed by the European Medicines Agency and regulatory agencies across the world, the effects of injection of these highly modified synthetic pseudo-mRNA have not been adequately investigated. This includes effects on human immunology, autoimmunity, toxicity, pharmacokinetics (how long an active drug stays in the body), pharmacodynamics (study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs), pharmacodistribution (where a drug goes in the body) and clearance (how long and by what mechanisms a drug takes to be broken down and removed from the body).
The willful avoidance and ignorance by FDA and Pharma concerning these key parameters is what underlies the misinformation propagated by FDA, Pharma, and mRNA vaccine advocates concerning where these molecules go in the body, how long they last, and how they are eliminated from the body. All of these issues have become common questions and concerns asked by patients to physicians and other allied health practitioners. But there are no solid, rigorous, methodical prospective study data to which health practitioners can refer to when answering their patient’s questions. All that is available are general platitudes promoted as propaganda by Pharma, the Government, and academic stakeholders such as Drs. Kariko and Weissman (and the Nobel Prize Selection Committee) who have repeatedly, and incorrectly asserted that these synthetic foreign pseudo-mRNA are rapidly degraded in the body after injection. Subsequent research by laboratories from all over the world have demonstrated that this is a false statement - mis- or dis-information - and that these synthetic molecules persist in the bodies of injected persons for weeks to months, rather than the hours originally asserted.
The inconvenient truth in this matter is that current scientific understanding of the molecular biology, immunology and toxicology of both Pseudouridine - modified mRNA as well as N1-methyl-Pseudouridine - modified mRNA is still in development. In plain words, not well understood at this point. What is clear is that these modified pseudo-mRNA have a wide range of biological effects, including immunosuppression. Which can be a good thing for overcoming one barrier (inflammatory response) to the medical administration of synthetic mRNA formulated into self-assembling lipid particles. But may well be a bad thing for things like autoimmune disease and the ability of the immune system to control other infectious disease and cancer.
Of additional relevance is that these pseudouridine and N1-methyl-pseudouridine modifications of synthetic mRNA are not necessary for eliciting an immune response to the protein encoded by such synthetic mRNA. This is clearly demonstrated in the initial reduction to practice (in mice) demonstrated by myself and others at the La Jolla startup biotech company Vical in 1990, and in the context of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine development by the initial clinical trial results of the European biotech startup CureVac. The pseudouridine (or N1-methyl-Pseudouridine) may make synthetic mRNA-based drugs and vaccines more potent on a comparative dose-by-dose basis, but it is not necessary and this effect may be overcome by increasing the dose of non-pseudouridine modified synthetic mRNA.
What is clear is that, for some reason, the FDA suspended its normal processes and procedures which would typically require that a biologically active new chemical entity be thoroughly investigated prior to use in humans. The reason and logic behind this gross negligence should be thoroughly investigated and disclosed to the public.
Both those who have received these poorly characterized products, often after being subjected to a wide range of psychological manipulation, propaganda, compulsion and coercion (mandates), and all too often with dosing-associated adverse events (including severe AE including death) deserve to know what happened and why.
Pseudouridine Facts
•Pseudouridine is a modified nucleotide mRNA subunit that is prevalent in natural human mRNAs
•The biologic significance and regulation of the pseudouridine modification process is still being determined and understood.
•This modification occurs naturally in the cells of our body, in a highly regulated manner. This is in sharp contrast to the random incorporation of synthetic pseudouridine which occurs with the manufacturing process used for producing the Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech (but not CureVac) COVID-19 “mRNA” vaccines.
•These modifications occur at locations associated with alternatively spliced RNA regions, are enriched near splice sites, and overlap with hundreds of binding sites for RNA-binding proteins.
•pre-mRNA pseudouridylation is used by human cells to regulate human gene expression via alternative pre-mRNA processing
•mRNA pseudouridylation may control mRNA metabolism in response to changing cellular conditions
•Incorporating RNA modifications, including pseudouridine, in foreign RNA allows for escape from innate immune detection
•Presence of modified nucleosides in viral genomic RNA could contribute to immune evasion during infection
•In vitro transcribed RNA is immunostimulatory when transfected into HEK293 cells engineered to express either TLRs and inclusion of Ψ in the RNA suppressed this response (most pronounced for TLR7 and TLR8).
• Inclusion of Ψ in a 5′-triphosphate capped RNA abolishes activation of RIG-I, providing another mechanism for pseudouridine-mediated suppression of innate immune activation.
•Pseudouridine likely affects multiple facets of mRNA function, including reduced immune stimulation by several mechanisms, prolonged half-life of pseudouridine-containing RNA, as well as potentially deleterious effects of Ψ on translation fidelity and efficiency.
For more detailed information and documentation relevant to the above discussion, please see the following peer-reviewed academic publications:
Yuri V. Svitkin, Yi Min Cheng, Tirtha Chakraborty, Vladimir Presnyak, Matthias John, Nahum Sonenberg
Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 2; 45(10): 6023–6036. Published online 2017 Feb 23.
N1-Methylpseudouridine substitution enhances the performance of synthetic mRNA switches in cells
Callum J C Parr, Shunsuke Wada, Kenjiro Kotake, Shigetoshi Kameda, Satoshi Matsuura, Souhei Sakashita, Soyoung Park, Hiroshi Sugiyama, Yi Kuang, Hirohide Saito
Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Apr 6; 48(6): e35. Published online 2020 Feb 24.
Karikó K, Muramatsu H, Welsh FA, Ludwig J, Kato H, Akira S, Weissman D.Mol Ther. 2008 Nov;16(11):1833-40. doi: 10.1038/mt.2008.200. Epub 2008 Sep 16.
Pseudouridine synthases modify human pre-mRNA co-transcriptionally and affect pre-mRNA processing.
Martinez NM, Su A, Burns MC, Nussbacher JK, Schaening C, Sathe S, Yeo GW, Gilbert WV.Mol Cell. 2022 Feb 3;82(3):645-659.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.12.023. Epub 2022 Jan 19.
Regulation and Function of RNA Pseudouridylation in Human Cells.
Borchardt EK, Martinez NM, Gilbert WV.Annu Rev Genet. 2020 Nov 23;54:309-336. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-112618-043830. Epub 2020 Sep 1.PMID: 32870730
Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications.
Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, He C.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Jan;18(1):31-42. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.132. Epub 2016 Nov 3.
The epitranscriptome beyond m6A.
Wiener D, Schwartz S.Nat Rev Genet. 2021 Feb;22(2):119-131. doi: 10.1038/s41576-020-00295-8. Epub 2020 Nov 13.
RNA modifications: importance in immune cell biology and related diseases.
Cui L, Ma R, Cai J, Guo C, Chen Z, Yao L, Wang Y, Fan R, Wang X, Shi Y.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Sep 22;7(1):334. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01175-9.
The emerging role of RNA modifications in the regulation of mRNA stability.
Boo SH, Kim YK.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Mar;52(3):400-408. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0407-z. Epub 2020 Mar 24.
Haruehanroengra P, Zheng YY, Zhou Y, Huang Y, Sheng J.RNA Biol. 2020 Nov;17(11):1560-1575. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1722449. Epub 2020 Feb 7.
Role of main RNA modifications in cancer: N6-methyladenosine, 5-methylcytosine, and pseudouridine.
Xue C, Chu Q, Zheng Q, Jiang S, Bao Z, Su Y, Lu J, Li L.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Apr 28;7(1):142. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01003-0.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 4:9:789427.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.789427. eCollection 2021.
The Critical Contribution of Pseudouridine to mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines
Pedro Morais 1, Hironori Adachi 2, Yi-Tao Yu 2
Free PMC article
Abstract
The current COVID-19 pandemic is a massive source of global disruption, having led so far to two hundred and fifty million COVID-19 cases and almost five million deaths worldwide. It was recognized in the beginning that only an effective vaccine could lead to a way out of the pandemic, and therefore the race for the COVID-19 vaccine started immediately, boosted by the availability of the viral sequence data. Two novel vaccine platforms, based on mRNA technology, were developed in 2020 by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Therapeutics (comirnaty® and spikevax®, respectively), and were the first ones presenting efficacies higher than 90%. Both consisted of N1-methyl-pseudouridine-modified mRNA encoding the SARS-COVID-19 Spike protein and were delivered with a lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulation. Because the delivery problem of ribonucleic acids had been known for decades, the success of LNPs was quickly hailed by many as the unsung hero of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. However, the clinical trial efficacy results of the Curevac mRNA vaccine (CVnCoV) suggested that the delivery system was not the only key to the success. CVnCoV consisted of an unmodified mRNA (encoding the same spike protein as Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech's mRNA vaccines) and was formulated with the same LNP as Pfizer-BioNTech's vaccine (Acuitas ALC-0315). However, its efficacy was only 48%. This striking difference in efficacy could be attributed to the presence of a critical RNA modification (N1-methyl-pseudouridine) in the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna's mRNA vaccines (but not in CVnCoV). Here we highlight the features of N1-methyl-pseudouridine and its contributions to mRNA vaccines.
<Note that the dose of CVnCoV used in these studies was lower than that of either comirnaty® and spikevax®>